QVANTUM supports the calculations and formulas defined on this page. Unless otherwise described, you can use them both in the model and in user-defined columns.
Calculation operations
Addition (+)
Subtraction (-)
Multiplication (*)
Division ( / )
Round parentheses
References to other dimension elements
Unless otherwise described, square brackets set key figure keys (e.g. in the form ABS([DELTA])) or constants are used for the arguments of a function in key figure formulas.
For user-defined row or column definitions in forms, row or column identifiers (e.g. ABS([3]) or ABS([B])) or constants enclosed in square brackets are used for the arguments of a function.
In principle, formula expressions formed from the named specifications can also be used, possibly using parentheses (e.g. ABS(([A]-[B])/[C])).
Function calls are also allowed in the formula expressions (e.g. ABS(DIVIDE([1];[2];BLANK)).
The names of functions are case-insensitive.
When dividing by zero, the value UNVALID is generated, unless the function DIVIDE (see below) is used for the division.
Empty cells have the value BLANK.
An evaluated condition (see IF function) has the value TRUE, if it is fulfilled otherwise FALSE.
For example:
Key figure revenue = [US]*[PPU]
US = Key of "Units sold"
PPU = Key of "Price per unit"
Formulas and functions
ABS
The function calculates the amount of a number.
Syntax:
ABS(<argument>)
Special cases:
- Value of UNVALID = UNVALID
- Value of BLANK = BLANK
COALESCE
Returns the first expression that does not evaluate as BLANK. If all expressions evaluate to BLANK, BLANK is returned. The function has at least 2 or more arguments.
Syntax:
COALESCE(<argument1>); <argument2> [;<argument3>...])
DIVIDE
Performs a division and returns an alternate result or BLANK if dividing by 0.
Syntax:
DIVIDE(<div>; <divisor> [;<alternative result])
The alternative result for a division by 0 must be a constant. If the specification is missing, the result for division by 0 is BLANK.
Special cases:
- UNVALID / x and x / UNVALID results in UNVALID
- BLANK / BLANK results in BLANK
- x / BLANK gives the alternative result
- x is an arbitrary valid number
ROUND
Rounds a number to the specified number of digits.
Syntax:
ROUND(<argument> [; <number of digits>)
Use <argument> to specify which number to round. The number of digits is the number of decimal places to which you want to round. For a negative value, digits to the left of the decimal separator are rounded. If the value is 0 or if the number of digits is not specified, the number is rounded to the nearest whole number. The number of digits must be a constant.
SIGN
Determines the sign of a number. The function returns 1 if the number is positive; 0 if the number is 0; or -1 if the number is negative.
Syntax:
SIGN(<argument>)
Special cases:
- Value of UNBALANCED = UNBALANCED
- Value of BLANK = BLANK
IF
Checks a condition and returns a value if it is TRUE; otherwise returns a second value.
Syntax:
IF(<condition>;<value if TRUE>;<value if FALSE>)
<Condition> is composed of an <argument1> and an <argument2> separated by a comparison operator. The comparison operators allowed are:
<, <=, >, >=, =, <> or !=.
Special cases:
If <argument1> or <argument2> are empty, the argument is interpreted as 0.
TIME SUBSTITUTION
This function allows a predecessor element of the time dimension to be accessed in a ratio formula.
Syntax:
TIMESUBSTITUTION(<argument>;<relative predecessor>)
The prerequisite is the definition of a dimension with the dimension role time. Typically, this is the months. The function acts only on the leaves (lowest level) of this dimension.
The <argument> must be a key figure, a formula expression is not allowed. The function is not available in form formulas.
The <relative predecessor> is a negative constant and denotes the step size to be able to determine the predecessor element.
The predecessor element is the leaf higher up in the order of dimension elements relative by the specified step size. Elements which are not leaves are not counted. The function does not work according to the order of the dimension elements on the 1st sheet, which is also not capable of input. Therefore, the start value must be entered in another key figure. A formula for a key figure x can exceptionally use the target key figure x as an argument in the TIME SALES function (e.g. in the sense of [NUMBER_CUSTOMERS] = [CUSTOMER_INFLOW] + TIME SALES([NUMBER_CUSTOMERS];-1)).
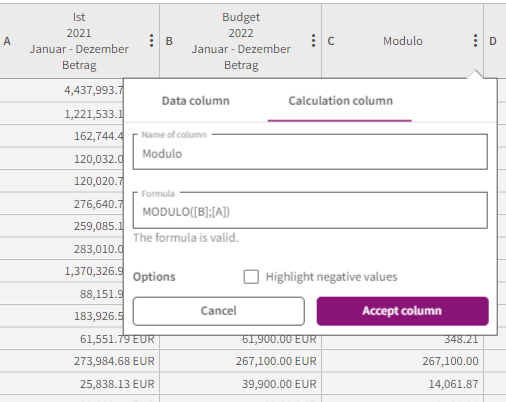
MODULO
Modulo returns the remainder of an integer division.
Example:
15 mod 12 = 3, since 15 : 12 = 1, 3 remains.
Syntax:
MODULO(<dividend>; <divisor>)
Example:
In the following example the formula MODULO([B];[A]) was used.
QUOTIENT
Forms the quotient of divisor and divisor. An integer is always returned.
Syntax:
QUOTIENT(<divider>; <divisor>)
Example:
QUOTIENT(5;3)
The result is 1, because the decimal places are omitted.
The following functions are still in preparation:
MIN/MAX (returns minimum value or maximum value from a list of parameters)
BLANK (returns empty value, e.g. to leave cells empty in case of a WHEN function)